AI in Test Automation: Benefits, Tools & Future Trends to Know

In today’s fast-paced software development world, quality assurance (QA) and test automation are undergoing a major transformation thanks to artificial intelligence (AI). What used to be repetitive, maintenance-heavy test automation is evolving into intelligent, adaptive, autonomous testing. Below is a deep dive into how AI is shaping test automation: the benefits, the tools leading the charge, and the trends you’ll want to watch (and act on) in 2025 and beyond.
Why AI in Test Automation? Key Benefits
The adoption of AI in test automation brings several significant advantages:
1. Faster test generation and execution
AI-driven tools can analyse code, user behaviour, and UI changes to auto-generate test cases, dramatically reducing manual effort.
For example, tools now generate test cases from natural language or from existing scripts, accelerating coverage.
2. Improved test coverage & defect detection
Machine-learning models can prioritise which parts of the application are likely to fail (based on historical data) and steer testing toward high-risk areas.
This means fewer surprises in production, better quality, and potentially fewer customer-facing issues.
3. Reduced maintenance overhead via self-healing tests
One of the big headaches in automation: when the UI or API changes, tests break. AI tools can now detect these changes and “self-heal” or update the test scripts accordingly.
This frees up QA engineers from endless script updates and lets them focus on more strategic testing.
4. Better integration with DevOps and continuous testing
AI helps embed testing earlier in the development lifecycle (“shift-left”) and supports continuous testing pipelines.
By doing so, feedback loops shorten, bugs are caught earlier, and overall time-to-market is improved.
5. Empowerment of broader teams via low-/no-code
AI-augmented tools increasingly provide natural-language test creation, codeless automation, or low-code interfaces — making test automation more accessible beyond specialised QA engineers.
In summary: AI in test automation isn’t just a nice-to-have; it’s becoming a competitive necessity if you want faster release cycles, higher quality, and leaner test operations.
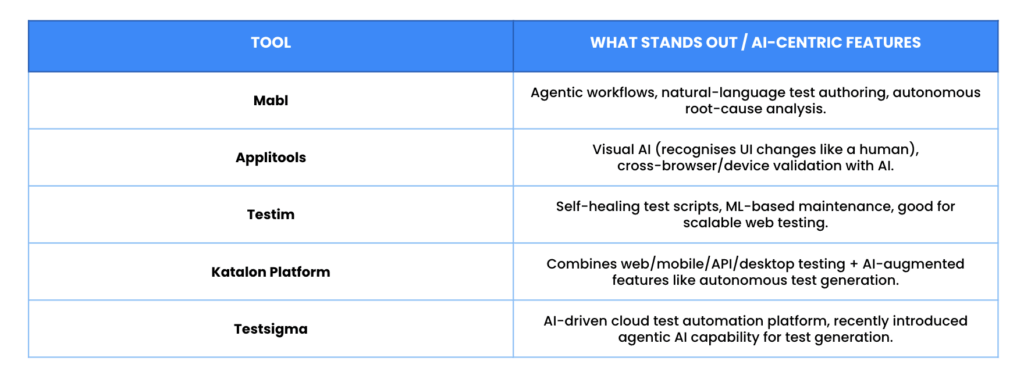
Key Tools and Platforms to Look At
Here are some of the leading tools (and tool features) in the AI-driven test automation space. Note: this isn’t an exhaustive list, but it gives a good cross-section of what’s happening.
Some feature trends in these tools
- Natural-language test definitions (“Write this scenario in plain English and I’ll generate the test”)
- Autonomous agents: the tool can decide which tests to run, when, how, and adapt as the application evolves.
- Visual AI: tools that “see” the app’s UI just like a human would (detecting layout shifts, styling issues, etc).
- Predictive analytics: metrics and ML models that forecast which modules are defect-prone and need more testing effort.
- Self-healing: fewer broken scripts, lower maintenance.
- Low-/no-code interfaces: reduce dependence on specialised scripting skills.
Emerging Trends & What’s Coming Next (2025 and Beyond)
The AI-test-automation space is evolving quickly. Here are several key trends and what to watch.
1. Agentic AI and autonomous testing systems
“Agentic AI” refers to AI agents that operate with agency: they can interpret goals, reason, adapt, and act — rather than just follow scripted rules.
In the test automation context, this means: the AI selects which tests to run, adapts them as code changes, learns from outcomes, and suggests improvements.
One article cites that ~50% of companies aim to launch AI agents as proof-of-concept by 2027.
Another outlines “third wave” tools (2025-era) that go beyond just faster automation, into the reduction of maintenance burden via autonomous behaviours.
2. Self-healing, visual & predictive testing everywhere
2025 is seeing a surge in:
- Self-healing scripts that adapt automatically when UIs/APIs change.
- Visual-AI testing: UI issues, cross-device/cross-browser changes, dynamic content — AI can detect what human testers might miss.
- Predictive analytics: Using historical data, code changes, and usage logs to identify where bugs are likely to emerge and what tests should be prioritised.
3. Hyper-automation and end-to-end embedded QA
Testing is becoming fully embedded into the continuous delivery pipeline, not a separate phase. AI helps bridge testing across UI, API, microservices, performance, security, even UX.
We’ll see more “test-everything” strategies, with AI orchestrating across domains, tools and teams.
4. Shift in QA roles, skills & governance
AI doesn’t replace humans — but changes how they work. QA professionals are shifting from script-writers to orchestrators of intelligent systems.
Skills to watch: data analysis, prompt engineering, AI model understanding, and interpreting AI-driven test results.
Governance becomes important: transparency of AI decisions, ethical use (avoiding bias), data privacy, and auditability.
5. Integration with DevOps / Agile / CI/CD at a deeper level
Testing won’t just be automated — it’ll be continuous, real-time, and part of every code commit, facilitated by AI.
Feedback loops will shrink further, meaning faster releases and quicker detection of issues.
6. Low-/No-Code & democratisation of test automation
As AI enables natural-language test generation and low-code platforms, more non-QA roles (product owners, developers) will be able to author or trigger tests.
This democratisation helps organisations scale testing beyond specialist teams.
7. Emerging research & proof-of-concepts
For example, recent academic work introduced a generative AI‐based end-to-end test automation approach (“GenIA-E2ETest”), which translates natural language descriptions into executable E2E test scripts, achieving ~77% completeness and minimal manual modifications.
These proofs suggest the next frontier: more generative, more autonomous test creation and maintenance.
Challenges & Considerations (Because it’s not all smooth sailing)
It’s important to recognise what must be addressed to successfully adopt AI in test automation.
- Human oversight remains critical: AI tools may lack context, business understanding, or may misinterpret UX intent. Humans must still guide, review, and interpret.
- Data quality & training: Models for predictive analytics or generative tests need high-quality historical data; otherwise, outcomes may be skewed.
- Ethics, bias & governance: AI decisions (which tests to run, which defects to prioritise) must be transparent and auditable.
- Integration complexity: Embedding AI into existing toolchains, CI/CD pipelines, and workflows can be non-trivial.
- Change management: Teams must upskill, adapt to new roles and workflows; resist the “we’ll rely on AI blindly” trap.
- Maintenance of AI models: Just like any software, the AI layer itself needs monitoring, tuning, and updating as applications evolve.
Practical Tips for Getting Started
If your organisation is considering adopting AI in test automation, here are actionable steps to increase your chances of success.
1. Evaluate your automation maturity first
Audit your current test automation: coverage gaps, script maintenance burden, bottlenecks, repeat failures. This gives you meaningful targets for AI.
2. Identify high-impact use case(s)
Don’t try to boil the ocean. Start with high ROI areas: regression tests, UI/frequently changing components, modules with many bugs or high risk areas.
3. Run a pilot with an AI-powered tool
Choose 2-3 candidate tools (from those above or others). Create the same test scenario with each and evaluate on parameters such as ease of setup, maintenance cost, defect detection, and adaptability.
4. Upskill the team
Provide training on AI/test automation, data analytics, and prompt engineering (if generative tools). Ensure QA engineers understand how to work with AI, not just on AI.
5. Govern and monitor
Set up metrics: defect escape rate, test-script maintenance overhead, time to test, and ROI of automation. Monitor for AI drift, model performance, and integrate governance (data ethics, transparency).
6. Scale gradually
Once a pilot shows value, expand to more modules, integrate with CI/CD, and embed into DevOps workflows. Use lessons learnt to refine strategy and toolchain.
Looking Ahead: What to Watch in the Next 2-3 Years
- Fourth wave of AI in test automation: Some practitioners are already talking about moving beyond current “third wave” tools into even more autonomous, goal-oriented AI systems that require minimal human input.
- Generative AI for test creation: Natural-language → full test scripts, with minimal hand-coding, adapting as apps change. The GenIA-E2ETest research is an example.
- Greater convergence of QA, DevOps, and AI-Ops: Testing will become part of broader operations and AI ecosystems — not just QA’s domain.
- More focus on UX, security, performance testing via AI: AI won’t just do functional tests; expect intelligent load-testing, security-testing, and user-behaviour simulation.
- Democratisation of testing: As tools become easier to use (natural language, low code), more roles will author or trigger tests (product owners, business analysts).
- Embedded AI test agents within applications: Imagine the application itself having built-in test agents that monitor its health, trigger tests in production-like conditions automatically.
- Regulation and ethics scrutiny: As AI becomes more pervasive, expect more governance, regulation, and standards around AI-driven testing (especially for safety-critical domains).
Conclusion
The integration of AI into test automation is no longer a futuristic concept—it’s an evolving reality. For organisations serious about software quality, speed, and efficiency, AI-powered test automation offers transformative potential: less manual toil, smarter test coverage, faster releases, and better product stability.
However, successful adoption requires more than buying a tool. It demands thoughtful strategy: maturity assessment, pilot execution, team upskilling, governance, and continuous refinement. And perhaps most importantly, recognising that AI doesn’t replace testers—it augments them.
If you’re planning to modernise your QA practice, now is the time to explore AI in test automation. The trends for 2025 show acceleration, and those who start early could gain a significant advantage.